Types of Chemical Bonds
*Review: Understand that electronegativity (the ability of an electron to attract shared electrons to itself) increases to the right and up on the periodic table
A Chemical Bond is the attraction between the nucleus of one atom and the electron of another atom:
- Ionic Bonds: Transferring of an electron (usually involving a metal and nonmetal) - this generally occurs when the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is greater than 1.7
- While you do not need to memorize electronegativity values for the AP exam (any questions regarding specific values will give you them), you should remember the general trends of electronegativity on the periodic table covered in Unit 1.7 - Periodic Trends
- Covalent Bonds: Sharing of electrons
- Polar Covalent: Electrons shared unequally
- Nonpolar Covalent: Electrons shared equally - often only between di-atomic elements like O2
- Metallic Bonds: Electrons not associated with a single atom or molecule (Delocalized/Electron Seas)
You may see elements with low or high electronegativities be represented by δ+ and δ-, respectively. Dipole arrows will always point to the more electronegative element.
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about types of chemical bonds.
Which elements have the greatest difference in electronegativity?
Copper (Cu) and Zinc (Zn) are most likely to form which type of bond?
Sulfur (S) and Oxygen (O) are most likely to form which type of bond?
Gaseous Cl₂ employs which type of bonding?
Which statement best describes the difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Intramolecular Force and Potential Energy
Potential Energy Curves for covalent bonds represent the potential energy of a bond at various internuclear distances. The bond is stable when negative and most stable when highly negative (at equilibrium bond length). This would represent the two atoms being in an optimal range for bonding.
The bond is unstable when positive: this is when the atoms are so close that there is more repulsive force than attractive force. The distance from the x-axis to the lowest peak is the bond energy - the energy required to break the bond.
When comparing curves, double and triple bond curves will be more pronounced and have higher negative peaks because they are stronger.
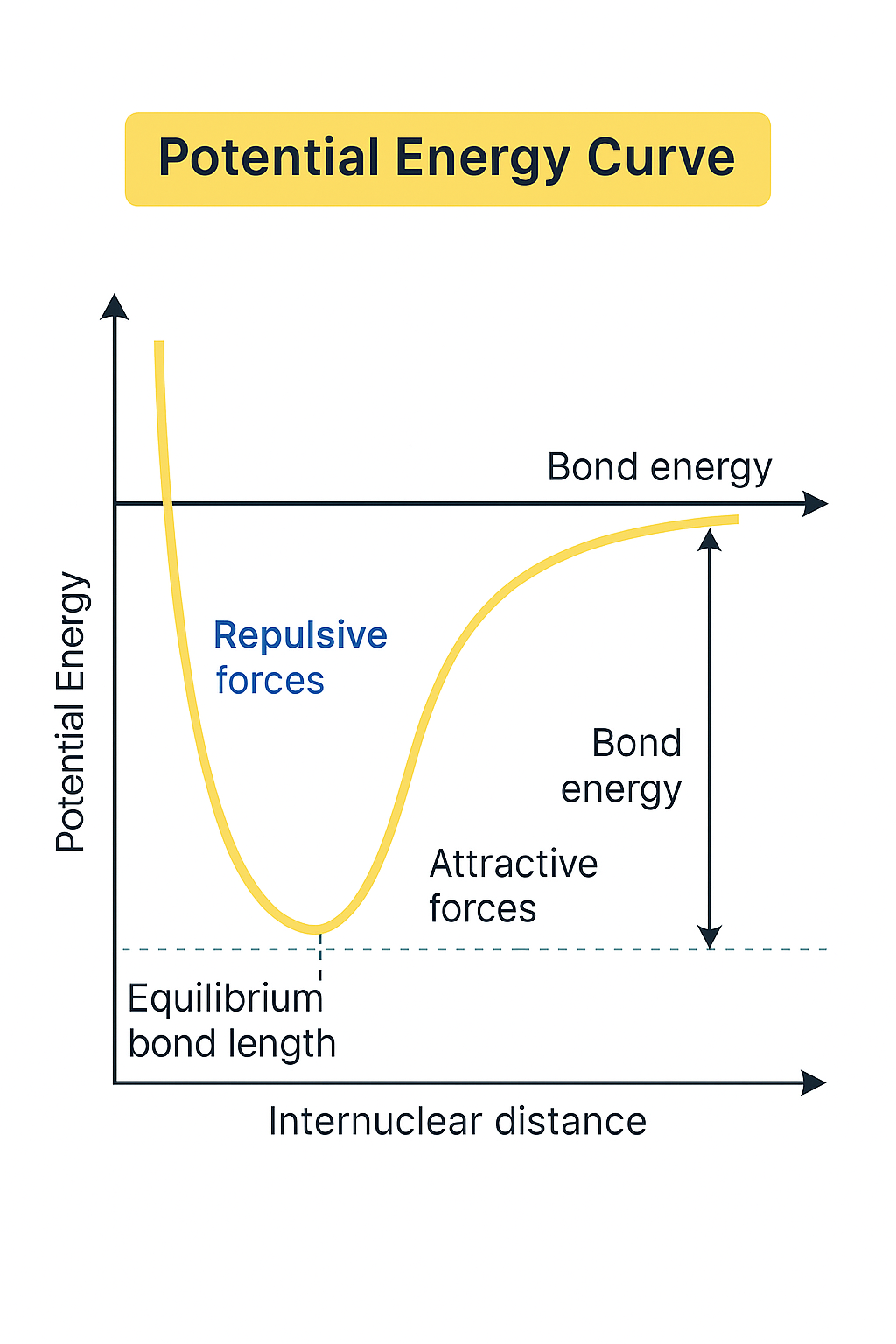
Most potential energy curves will follow this general trend.
Bonds may be formed in single, double, or triple forms, sharing either 2, 4, or 6 electrons. The more shared electrons produces a stronger bond
In ionic bonds, the attraction between cations and anions (positive and negatively charged ions) can be explained using Coulomb’s Law:
F = k (q₁q₂/r²)
Where q₁ and q₂ represent the charges on the ions, and r represents the distance between the two ions
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about intramolecular forces and potential energy.
Given the potential energy curve below, which point would have the highest attractive energy?
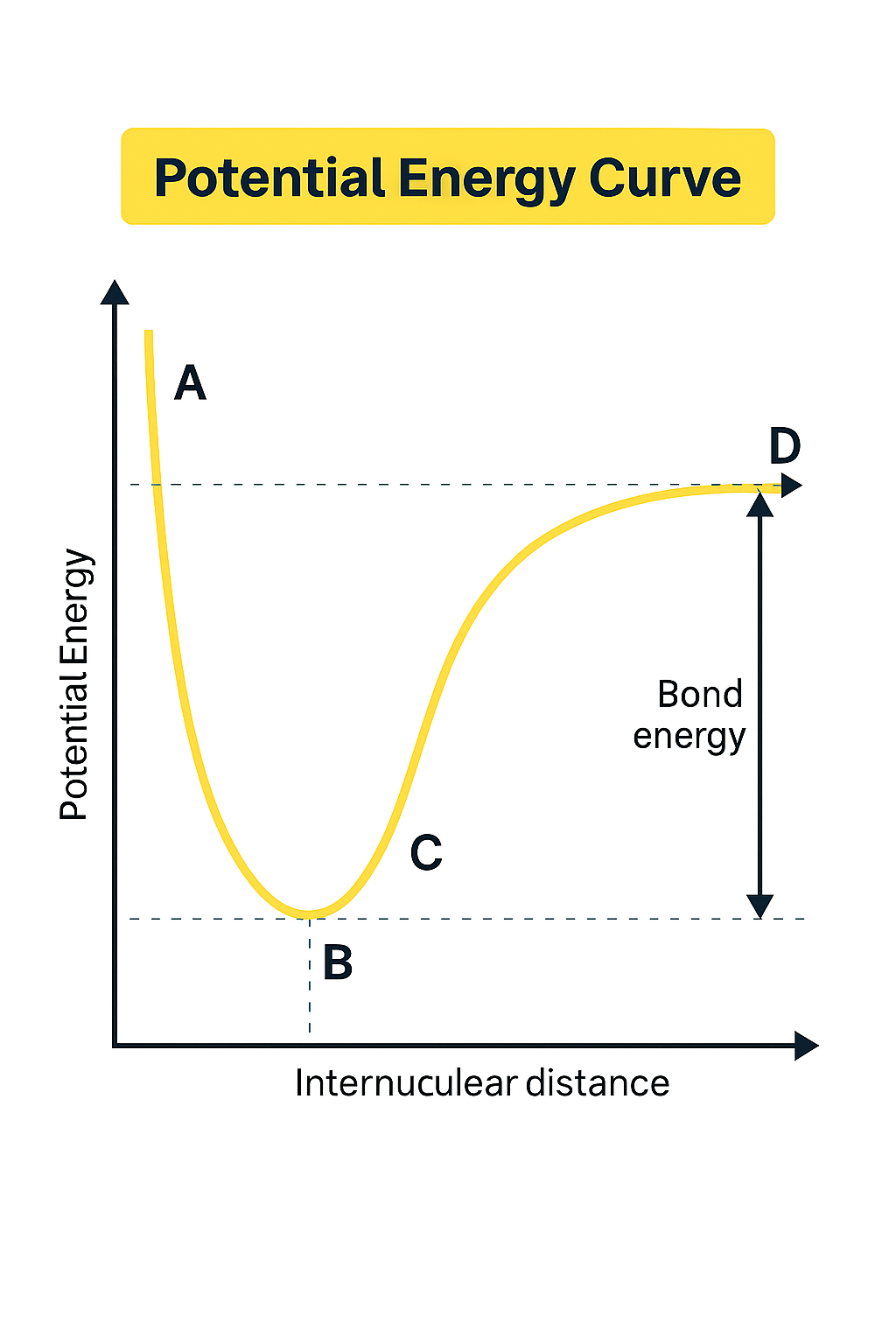
What best describes the forces present between two molecules at point C?

If the image shown below is the potential energy curve for a double bond, predict how point B will be effected if the bond is changed to be between 6 electrons

Structure of Ionic Solids
Ionic Compounds are the attraction between a cation (positive ion) and anion (negative ion).
In order for ionic compounds to conduct electricity, they must have charged particles and be free to move. Solid, crystal lattice structures cannot conduct electricity, while molten (melted) ionic compounds can effectively conduct electricity.
The crystal lattice structure will always have alternating cations and anions - and the radius/size of the ions must be taken into account if representing ionic solids.
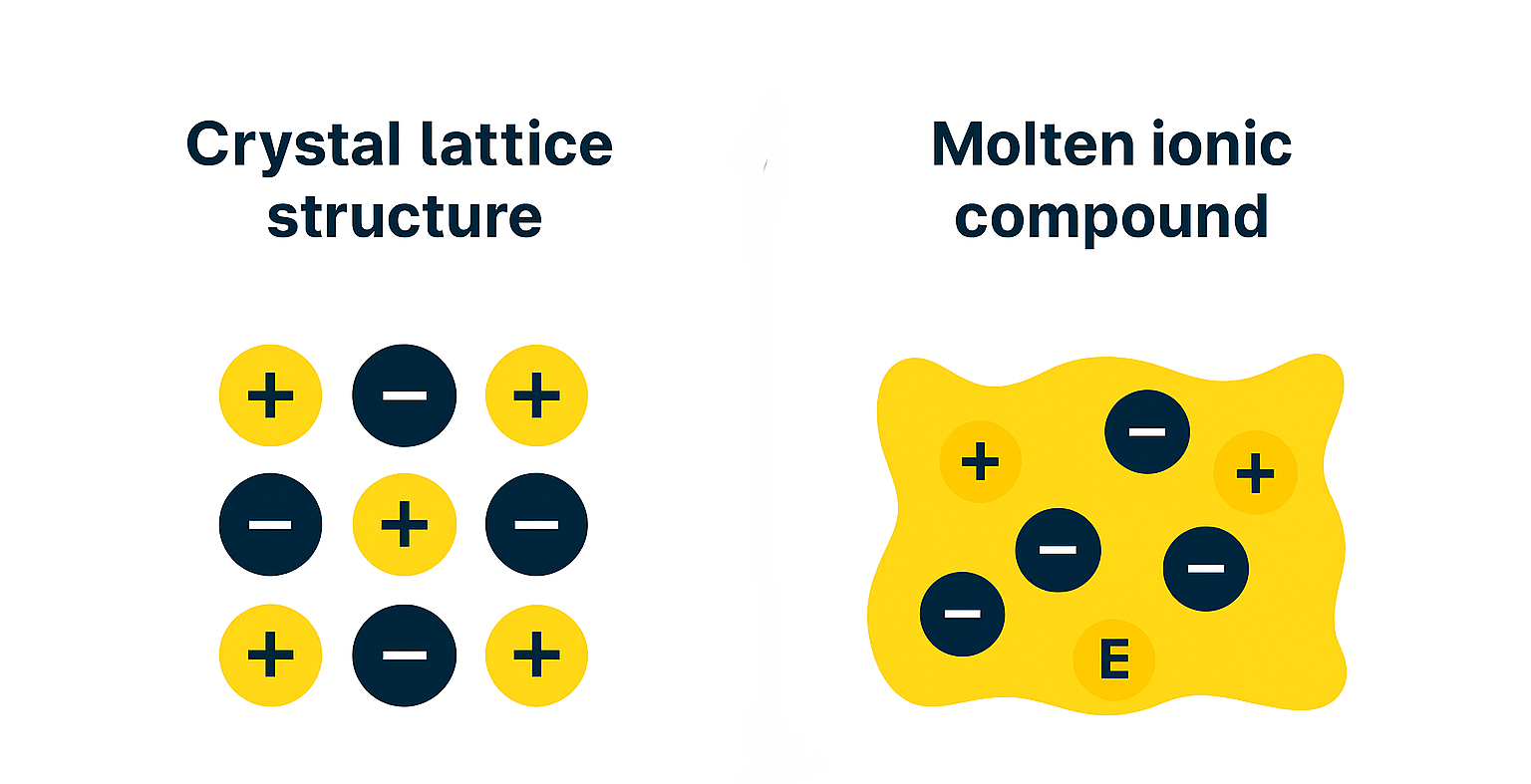
In solid form (left), ionic compounds are tightly bonded in a rigid structure. This prevents ions from moving freely and conducting electricity.
In molten form (right), ionic compounds have ions that are free to move around. This allows the substance to conduct electricity.
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about the structure of ionic solids.
In an ionic compound, the positive ion will be:
Which of the following substances is most likely to conduct electricity?
Structure of Metals and Alloys
In metallic bonds, positive metal ions are surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons. As a result, metallic bonds are good conductors of electricity, malleable, and ductile

Metallic Bonds have a delocalized sea of electrons. This allows the metal to conduct electricity and be malleable even as a solid.
Alloys are the combination of two or more metallic elements
- Substitutional Alloys have one metal substituting in for another in the crystal lattice. They must be of comparable radii. Ex: Brass = Copper and Zinc
- Interstitial Alloys have one metal that is much smaller atomic radii fill in the spaces between the larger metal atoms. These alloys are usually stronger than the base metal. Ex: Steel = Carbon in Spaces of Iron Atoms
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about the structure of metals and alloys.
The delocalized sea of electrons in metallic bonding promotes all of the following properties except:
Which of the following is most likely to occur between Titanium (Ti) and Nitrogen (N)?
What element is most likely to form a substitutional alloy with Nickel (Ni)?
Lewis Diagrams
Lewis Dot Diagrams may be used to represent molecules, showing bond order, unpaired valence electrons, and connectivity between atoms
In Lewis diagrams, the chemical symbol for atoms is used, along with dots to show electrons, or dashes to represent a bond
Alloys are the combination of two or more metallic elements
To construct a Lewis Dot Diagram, count the valence electrons (accounting for ions, either adding for a negative ion or subtracting for a positive ions), then determine the central atom (most electronegative atom) and place the rest of the atoms around it. Remember that single bonds require 2 electrons, double 4, and triple 6.
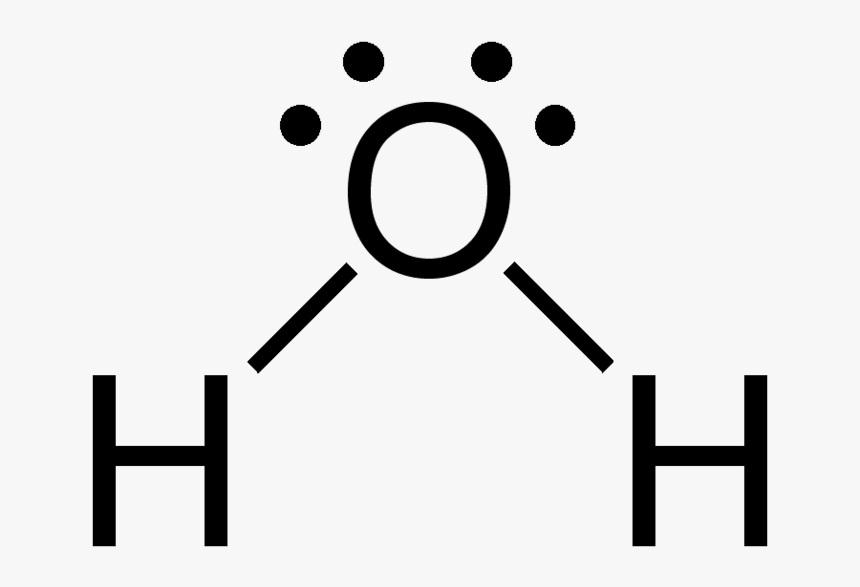
Lewis Diagram for H₂O. The most electronegative element is O, so it is the central atom.
The two dots above the O represent unbonded electron pairs - the dashes represent single bonds (double or triple dashes represent doble or triple bonds).
Note that atoms in period 3 and below may form expanded octets and have greater than 8 valence electrons.
More examples and a more detailed guide for Lewis Dot Diagrams coming soon...
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about Lewis diagrams.
In the Lewis Diagram for CCl₄ the central atom will have how many lone pairs of electrons?
The Lewis Diagram of NO₂⁻ has how many electrons in lone pairs and how many in bonding pairs?
Resonance and Formal Charge
While double bonds and triple bonds are shorter in length than single bonds, if a molecule has an instance where only 1 of several bonds is a different length, all bonds should be the same length
Resonance refers to the several correct representations of a molecule when this occurs. A hybrid structure may be used, showing bonds with a dotted line to indicate a hybrid structure - where bond lengths are roughly averaged.
In cases where multiple different diagrams may be made for a single molecule, formal charge should be utilized to determine the correct representation. The formal charge is the normal valence electrons an atom has, minus the actual valence electrons it has (counting 1 for each single bond). The most accurate diagram will have the least non zero formal charges.
More examples and a more detailed guide for Lewis Dot Diagrams and their resonance and formal charges coming soon...
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about resonance and formal charge.
Resonance structures refer to
VSEPR and Hybridization
Lewis Diagrams do not represent shape! Molecules are not flat, but 3D:
VSEPR, or Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion, states that the electrons will repel each other due to coulombic forces. Both bonds and lone pairs of electrons - electron domains - will repel each other because they are negative. Each bond order counts the same.
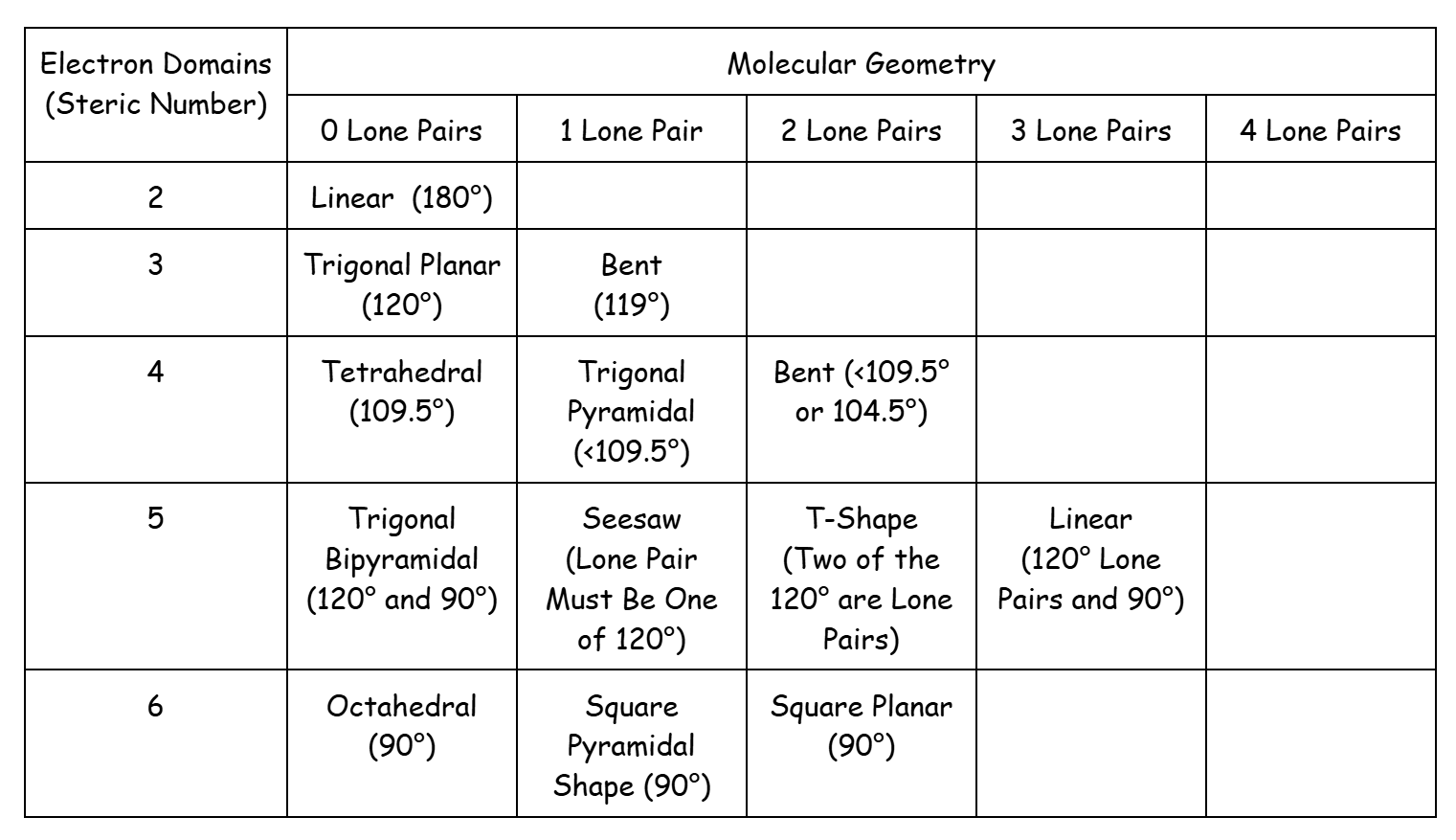
Common VSEPR shapes and angles. Note that you should memorize these shapes and angles for the AP exam.
Molecular Geometry Effects Polarity:
- If the bonds in a molecule are only nonpolar, no matter the shape, the molecule is nonpolar
- If the central atom is symmetrically surrounded by identical atoms, the molecule is nonpolar
- Symmetrical Shapes include Linear, Trigonal Planar, Tetrahedral, Trigonal Bipyramidal, Square Planar, and Octahedral
- Other shapes are not symmetrical, and any polar bond will make the molecule polar
When molecules form bonds, their orbitals form hybrid orbitals:
| Electron Domains | Hybridization |
| 2 | sp |
| 3 | sp² |
| 4 | sp³ |
| 5 | sp³d |
| 6 | sp³d² |
Check Your Understanding:
Try this quick quiz to reinforce what you just learned about VSEPR and hybridization.
Angles of 120 degrees are characteristic of all of the following molecular geometries except:
Methane (CH₄) has which molecular geometry?
Which of the following molecular geometries would most likely indicate a polar molecule?
A molecule with only 2 electron domains always has which molecular geometry?
A molecule with 4 electron domains has which of the following hybridizations?